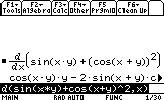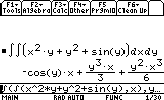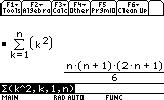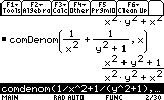TI-89 Tutorial
March 21, 2003
Updated on April 16, 2006
The TI-89 is a great calculator, it's one of the best calculators right now (there's the HP-49G which is a good calculator too, the TI-92 Plus offer the same specifications as the TI-89 but offers Geometry possibilities with the Cabri Géomoètre and the Geometer's Sketchpad).
For the latest and most up-to-date tutorial download this tutorial in PDF format: ![]() TI-89 Tutorial
TI-89 Tutorial
For any suggestions or feedback click here.
- Equations & system of equations
- Limits, sums & Taylor expansions
- Number operations
- Sequence
- Derivation & integration
- Polynomials
- Differential Equations
Top Solving equations & system of linear equations:
- Suppose we want to solve the following equation:
-3x3 +3 x2 -2x+5=0
The syntax is :solve(-3x^3+3x^2-2x+5=0,x)
or
zeros(-3x^3+3x^2-2x+5,x)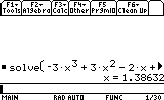
I have written ",x" after the equation because the variable to solve for in this equation is x
- Suppose we want to solve the following system
of equations:
2x-3y+5z=-1
-3x+5y-2z=3
5x-7y+8z=-2
Top Derivation & Integration:solve(2x+3y+5z=-1 and -3x+5y-2z=3 and 5x-7y+8z=-2,{x,y,z})
or
zeros({2x+3y+5z+1 ,-3x+5y-2z-3 ,5x-7y+8z+2},{x,y,z})
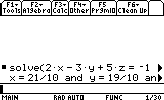
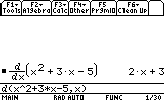
- Derivation
Suppose we want to compute the derivative of : x2+3x-5
The syntax isd(function,variable,degree)
degree can be omitted,it's 1 by default
Compute the partial derivative fx of f(x)=sin(x*y) +cos2(x+y)
- Integration:
Let's say we want to integrate the function sin(x):
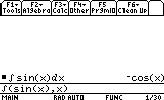
Top Limits, sums & Taylor expansions
Compute the double integral of : [x2 y + y2 +sin(y)] dxdy (we integrate for x supposing y constant then we integrate for y supposing x constant)
Let's say we want to calculate the value of the integral of x*cos(x) between 1 and 10:
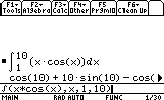
- Limits
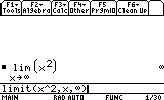
Suppose we want to compute the limit of x2 when x tend to infinity
The syntax is:
lim(function,variable,point,direction)
direction is both 1 and -1 and can be omitted
1: limit from right
2: limit from left
- Sum:
sum k2 for k between 1 and n
- Taylor expansions:
The syntax for computing Taylor series is:
taylor(function,variable,degree,point)
point can be omitted , it's 0 by defaultSuppose we want to know the 6th degree Taylor expansion of sin(x) around 0:
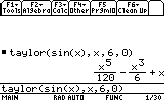
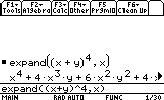
- Expanding polynomials
The syntax is
expand(polynomial,variable)
Let's say we want to expand (x + y)4
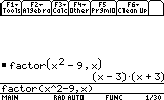
- Factoring polynomials
The syntax is:
factor(function,variable)
Let's factor the function x2-9
- Common denominator:
Top Number operations:Let's put on the same denominator the function: (1/x2)+(1/(y2+1))
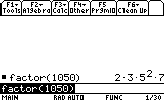
- Factoring a number:
factor(number)
Let's factor the number 1050 for example:
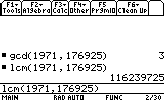
- Finding the GCD (Great Commun Divisor) & LCM (Least Commun Multiple) of 2 numbers:
gcd(number1,number2)
lcm(number1,number2)GCD & LCM of many numbers:
Let's find the GCD & LCM of 3 numbers:gcd(gcd(number1,number2),number3)
lcm(lcm(number1,number2),number3)
- Testing if a number is prime or not
isPrime(number)
Let's see if 997 is prime or not
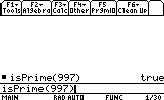
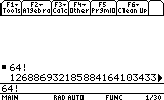
- Finding the factorial of a number:
Top Differential EquationsLet's find : 64!
Top SequenceLet's solve the following differential equation: x''+w2x=0
deSolve(function,x,y)
We must rename x to y
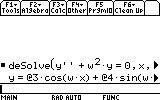
Note that the result is: @3 cos (w.x)+@4 sin(w.x)
@3 and @4 are constants
Suppose we want to find the terms of the following
sequence: Un+1=2*Un+2 with
U0=2
We can use 2 methods : the when function or by using
the Sequence mode of the calculator.
1. when() function
-
The syntax of this function is :
when(condition,true value,false value,unknown value)
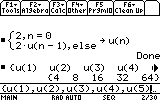
false value & unknown value can be omitted.when(n=0,2,2*u(n-1)+2) ->u(n)
The sign " -> " is to store the function in u(n)
To compute u, we write : u(1)

Suppose we want to find the 5 first terms of the sequence, we should write:
{u(1),u(2),u(3),u(4),u(5)}
- 2. Using the Sequence mode:
-
Let's take the previous example:
The syntax is:
u1=2*u1(n-1)+2
ui1=2
ui1 is the initial term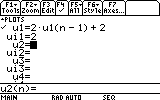
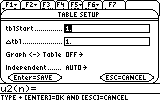
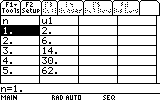
Note that the table start at 1 so en u0 is equal to n=1 on the calculator ,there is a shift of 1 between the calculator and the real world.